Describe the Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
A Marginal product of the last worker hired is less than the marginal product of the previous worker hired. The law of diminishing returns states that as one input variable is increased there is a point at which the marginal increase in output begins to.
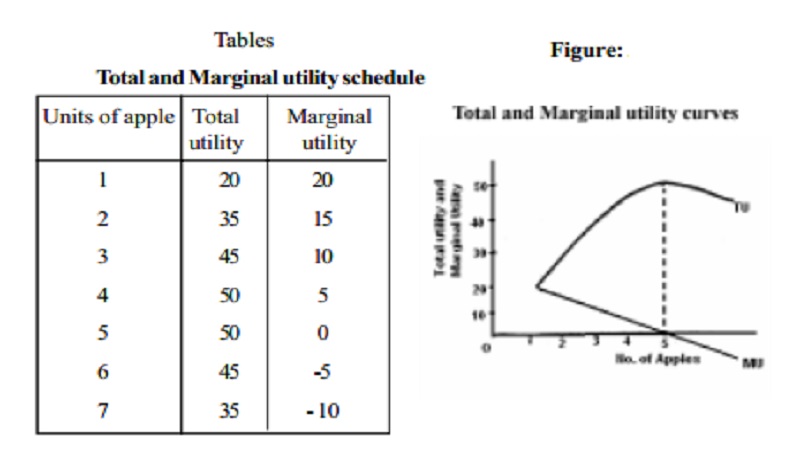
Law Of Diminishing Marginal Utility Dmu Definition Explanation Importance Criticism
Factor of Production Any input that generates a desired quantity of output.

. This is a rule of thumb that is used as an assumption to support many economic models and theories. B Marginal cost of the last worker hired is less than the marginal cost of the previous worker hired. Therefore the fall in marginal utility as consumption increases is known as diminishing marginal utility.
The marginal utility of pizza is 20 utils and its price is 2. See the fist chapter of this paper. The marginal utility derived from the product being consumed is not affected by the marginal utility derived from consuming similar goods or.
Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility. The operation of deducing one function from another according to some fixed law called the law of derivation as the of differentiation or of integration. The expected utility theory takes into account that individuals may be risk-averse meaning that the individual would refuse a fair gamble a fair gamble has an expected value of zeroRisk aversion implies that their utility functions are concave and show diminishing marginal wealth utility.
Explain the concept of price income cross elasticity of demand. C Average cost of the last worker hired is less than the average cost of the previous worker hired. Law of diminishing marginal utility.
The law of demand in economics pertains to the derivation and recognition of a consumers relative desire for a product or service coupled with a willingness and ability to pay for or purchase that good. Diminishing marginal returns refer to a situation in which the. Describe the steps and criteria in demand forecasting.
In the graph above Y 2-Y 1 is the marginal product. In the context of cardinal utility economists postulate a law of diminishing marginal utility which describes how the first unit of consumption of a particular good or service yields more utility than the second and subsequent units with a continuing reduction for greater amounts. 2 Law of diminishing marginal returns This law is necessary in order to define the optimal quantity to produces under the assumption that all that is supplied is sold at the given prices.
The Law Of Diminishing Marginal Utility is a fundamental principle of Economics that states that as consumption increases marginal utility declines. Marginal Product With every additional input the increase in total product is referred to as the marginal product. The law of diminishing marginal utility states that as consumption increases the marginal utility derived from each additional unit declines.
Diminishing marginal utility is a law of economics stating that as a person increases consumption of a product while keeping consumption of other products constant there is a decline in the marginal utility that person derives from consuming each additional unit of that product. The risk attitude is directly related to the curvature of the utility function. The crucial point of consumer preference theory is this law.
What do you understand by the law of supply and exceptions to the law of supply. The Usefulness of Utility. Total Product When an input is applied through a.
In fact in modern industrial economy most of products are produced as much as they sell at fixed prices by the producers. More formally it means that the Marginal utility of a commodity declines as successive units of it are consumed. Quantity demanded is used in.
It states that the more a product or service is consumed the lower the marginal utility is derived from consuming each extra unit. Describe total utility and marginal utility. For examples of diminishing marginal utility refer here.
The law of diminishing marginal utility describes this effect where adding one more unit of something typically results in fewer and fewer gains in utility for the consumer. With regard to the law of diminishing returns only one factor at a time is considered. Explain the law of diminishing.
There are exceptions to this rule. For example a inline skating enthusiast needs exactly 8 new wheels to get back into. If you buy 1 unit of each good will you achieve consumer equil.
Explain the meaning of indifference curve and list its properties. It states that as more and more of a commodity is consumed consumers receive less and less satisfaction from its consumption. Suppose the marginal utility of coke is 15 utils and its price is 1.

06 Law Of Diminishing Marginal Utility Youtube

What Is Law Of Diminishing Marginal Utility Definition And Meaning Business Jargons
Concept Of The Law Of Diminishing Marginal Utility Assignment Point

Upsc Cse Gs Law Of Diminishing Marginal Utility Offered By Unacademy
Comments
Post a Comment